A recession is technically defined as two consecutive quarters of the fiscal year with a decline in the gross domestic product, or GDP, of a given nation. A healthy economy expands over time, so two quarters in a row of contracting output suggests there are serious underlying problems, according to Shiskin. In 1974, economist Julius Shiskin came up with the definition of a recession, and it has become a common standard over the years.

GDP is similar to a receipt for an economy. It includes all the goods and services produced and sold in an economy over a year, combined into one big number. GDP measures the size of the economy, production, and overall efficiency.
A recession is a situation where a country experiences a slight fall in economic activity for months or years. It is, of course, a normal occurrence that can take place from time to time. Recession is synonymous with economic challenges where people are laid off, business activity is low, and the economy experiences a downturn.
Capitalism
In the past, during agrarian times, capitalism was different compared to what it is today. There were fluctuations regarding the pace of economic growth from year to year, but the rate of GDP growth was still quite stable. The economy was mostly defined by farming, therefore, it didn’t show the expected growth. Farming, in turn, was influenced by unpredictable events such as weather variations, diseases, and wars.
For instance, events in history such as the Black Death, which killed 40% of the population of Europe, or the Great Frost, which resulted in crop destruction, led to the contraction of the economy for a few years.
During the industrial revolution, people were prompted to produce more goods and do it more efficiently. They laid down new economic regulations, which made it profitable for those who invented, made, and sold the products, which improved the lives of both the seller and the buyer. This new economic system was known as capitalism.
Capitalism is effective because it encourages individuals to create improved products and businesses each year, increasing productivity and boosting the GDP annually. This will boost the production and sales of goods and thus expand the country’s economy.
There is a downside to the capitalist system. If the GDP does not increase, negative consequences will occur. A predictable pattern emerges as the GDP fluctuates every few years, resulting in a temporary decrease in the production and sale of goods. This phenomenon, which is not always linked to external factors like weather or war, is called a recession. It indicates a decrease in the number of products that can be manufactured and sold. A strong economy gradually grows over time despite experiencing fluctuations. Nevertheless, if it drastically drops in two consecutive quarters or more, it signifies serious problems in the economy.
The Business Cycle
This is a kind of curve that represents the concept of how the output of products and services fluctuates over time. It consists of four stages: expansion, peak, contraction, and trough.
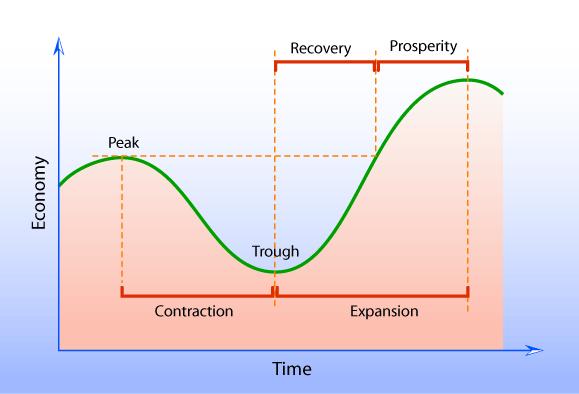
An economic expansion is a positive trend when businesses are making profits and the economy is thriving. During this time, consumer spending goes up, production and output increase, there is an increase in wages, and there is a decrease in unemployment.
A peak is the highest point between the end of an economic expansion and the start of a contraction in a business cycle.
An economic contraction is a drop in the business cycle caused by a slowdown in economic activity. It is characterized by reductions in individuals’ expenditures, decreases in manufacturing and output, falls in wages, and increases in unemployment.
The trough is the opposite of the peak. This stage marks the end of a period of declining business activity and the transition to expansion.
Boom, recession, and depression
These are the more severe stages of the business cycle.
During a boom, the economy is characterized by a high growth rate. All businesses operate at full capacity or even beyond capacity, with the jobless rate extremely low. Income and production are at their maximum, and this often leads to a sharp rise in prices.
A recession is a downward trend in the economy when the production of goods and services declines for a given period (many months). The rate of unemployment shoots upward as many people lose their jobs.
A depression is an extreme form of recession. It is a serious economic crisis characterized by a falling economy and a high rate of unemployment.
Impact of a Recession on Daily Life
Imagine you start hearing rumors of an upcoming economic recession due to a war happening somewhere. You decide it’s best to save money instead of splurging on expensive bread. Your neighbors are also noticing these signs and opting to make their bread at home since they find store-bought bread too costly. Finally, demand at the bakery is dropping. The amount of bread that people want to buy is less than the bread that the sellers have. This may lead to problems in the local bread market.
The bakery had hired too many employees when business was good, but now they cannot afford to keep them all because of low revenue. Consequently, they have no choice but to decrease their wages or even fire some employees.
One evening, your neighbor looks sad and informs you that they lost their job. This situation makes you anxious and helps you realize that you need to regulate your expenses better. The impact of these job losses is now beginning to affect others as well.
The decision to stop purchasing bread has made the workers in the bakery redundant, which in turn has led to a decrease in their income and expenditure. This reduction in spending affects other businesses (like the suppliers of the bakery), resulting in less revenue for them to pay their employees.
With this news spreading everywhere, other people also get cautious about spending money, thereby decreasing the number of transactions, lending, and investment. This downward spiral is making it increasingly difficult for the economy to function as it used to, with fewer products being manufactured and sold. Overall, the economy is shrinking, and the GDP shows a lower value than last year, meaning that the country is now in a recession.
What causes recessions?
1. Sudden economic shocks
These are unforeseen economic challenges that cause immense financial damage, e.g., natural disasters, wars, or geopolitical disputes. An illustration is when OPEC stopped supplying oil to the U.S. without notice in the 1970s. The coronavirus pandemic also led to a global economic shutdown.
2. Asset bubbles and excessive debt
Sometimes people make investment choices based on their feelings. Such choices usually lead to negative economic outcomes. During a period of economic growth, investors may become overly confident. They borrow too much money, thinking that the booming economy will help them handle the additional debt.
However, things will get bad if the economy slows unexpectedly and they find themselves struggling to manage the increased debt. Furthermore, the interest charges on their debts may be so high that there is no money left to cover their everyday expenses. This could lead to a rise in the number of people who have no choice but to default on their loans and go bankrupt, resulting in the collapse of the economy.
In the early 2000s, many firms in the tech industry got a lot of cash thrown at them, even if they were not doing fine. Such a situation is a bubble and will burst sometime in the future. When a bubble breaks, investors rush to withdraw their funds from the market in an attempt to minimize their losses.
The collapse in 2008 was mainly due to individuals and companies in the mortgage and housing industries taking on too much bad debt.
3. High inflation or deflation
these two principles are just changes in the value of a nation’s currency. Neither of them is either good or bad. They are always tied to the prevailing economic situation.
Inflation is a phenomenon in which the prices of products or services increase because of the increase in the amount of money available in the market. Whereas deflation is a fall in the money supply in the economy.
A low inflation rate is believed to boost economic activity. On the other hand, hyperinflation without increased demand can result in severe economic problems and might cause a recession. If inflation spirals out of hand, a currency loses its value.
Deflation can become more severe if it spirals out of control. It happens when the price keeps lowering due to a cash shortage. This will result in a decline in wages and a further decrease in prices. Such a downward cycle leads to a decrease in expenditure by both individuals and businesses, which harms the economy.
4. Technological advancements
Technological progress brings improved efficiency and long-term economic benefits. However, the introduction of innovations can pose short-term challenges. The Industrial Revolution eliminated numerous jobs, causing economic declines. Presently, some specialists worry that the implementation of AI and robots may lead to job cuts and potential economic downturns.
Recessions and the Business Cycle
During an economic expansion, the economy undergoes consistent and robust growth. Lenders facilitate easier and more affordable borrowing, prompting consumers and businesses to accumulate more debt. Asset prices start to rise due to irrational enthusiasm.
As the economy develops, the value of assets increases quickly, and people accumulate more debt. Eventually, during a certain phase of this cycle, an event like a war will disrupt economic growth. This disruption can lead to asset bubbles popping and the stock market crashing, and it becomes more difficult to handle large debts. Consequently, growth slows down, leading the economy into a recession.
Consequences of a recession
- People are making less money now, and hence, they spend less in the economy. This, in turn, decreases demand in the economy.
- The sales of businesses decline due to a decrease in demand, resulting in declines in income. Consequently, they can be forced to go bankrupt.
- The decline in sales and customer demand results in producers reducing the amount of goods and services they produce to match the lower demand.
- The reduction in income forces businesses to cut their employees’ pay due to economic struggles. In some cases, they have to lay off workers. Finding a new job becomes harder due to the surge in the number of unemployed people.
- If you fail to make those payments because your income has reduced or you have lost your job, you risk losing your home and other belongings.
- Lenders make it harder for people to get loans because many people struggle to pay their bills. You will need to improve your credit score or contribute a larger deposit to qualify for a loan when the economy is weak.
- All the money you had invested in shares, bonds, housing, or any other property might decline, which would mean a loss in your investments and savings and possibly affect your retirement plans.
What is the distinction between a recession and a depression?
Though both of them have the same roots, depression usually has more severe consequences. A depression has more job losses, higher unemployment rates, and stronger declines in GDP. Also, depressions can endure for years, unlike recessions that last months at most, and the economy takes a longer time to get back to its normal pace.
Can you predict a recession?
Predicting a recession or depression is challenging due to the complexity of modern economies. Some signs could be present due to some underlying conditions, like past economic activities. There could be a shift in market behavior toward recession. However, these events often have unforeseen triggers like the dot-com crash, housing collapse, or pandemic shutdowns, making prediction difficult without hindsight.
Conclusion
A recession is defined by two consecutive quarters of declining GDP which signifies underlying economic issues. The business cycle moves through stages of expansion, peak, contraction, and trough, with severe stages like boom, recession, and depression. Recessions impact daily life by reducing spending, causing unemployment, and affecting investments. Various factors like economic shocks, asset bubbles, inflation, deflation, and technological advancements can trigger recessions. Predicting recessions is challenging due to the complexity of modern economies. Understanding the distinctions between a recession and a depression is crucial, as depressions have more severe and lasting consequences. In such uncertain times, being vigilant and prepared can help navigate the challenges a recession may bring.


