Estate planning is the setting up, while you are alive of how your wealth, property and affairs will be protected, managed, and distributed or dealt with in the event of your death or incapacitation. An estate is everything you own, no matter how large or modest. For example your investments, assets like land and real estate, bank accounts, and interests.
Everyone has an estate, and you cannot take it with you when you die. I assume that, ideally, you would like to regulate how those things are delivered to the people and organizations of your choice. To ensure that your wishes are carried out, you need to provide a plan or instructions stating:
- who will eventually handle your responsibilities
- whom you want to receive, inherit, or benefit from your assets
- what you want them to receive, and
- when they are to receive it.
This plan will help reduce any uncertainties when it comes to the estate. You will want this transition to happen with the least amount paid in taxes, legal fees, and court costs. It takes the help of a qualified lawyer to assist you to choose the most suitable thing that will work for you.
Why is estate planning so important?
It helps to:
- Ensure that the distribution of wealth from older generations to the younger generations is done systematically according to their wishes.
- Protect your dependents, especially the minor ones, an incapacitated beneficiary or even the pets. This plan will have a guarantee of their care and financial support after you are gone.
- Ensure that the division of the wealth is in the manner you desire.
- Be very precise in your instructions. This will eliminate chances of confusion that may lead to conflict with the intended beneficiaries who include the members of the family.
- Avoid the process of succession. This is an expensive and laborious legal process that can be tiresome and complex to execute by your beneficiaries.
What should an estate plan do?
It should also do the following:
- Name the people or organizations you want to receive the things you own after you die.
- Include instructions on how you would like to be taken care of and your assets managed in the event you become physically or mentally incompetent before you pass on.
- Include:
- disability income insurance to cover your wages if you get sick or if you are injured and therefore cannot work,
- long term care insurance to assist with your bill in cases of an illness that may take a long time or if you are severely injured, and finally
- life insurance for your family after you are gone.
- Appoint a guardian for the upbringing of your children below the age of 18 and also for their inheritance.
- Take care of family members with special needs but do not make them lose the chance to receive government support.
- Provide for family members who may be financially reckless or for those warrant protection from creditors or in the event of divorce.
- Limit taxes, courts costs and other legal expenses. This might mean funding assets into a living trust, making or updating beneficiary designations. Otherwise, integrate your assets into your estate plan.
Who should plan for their estate?
Estate planning is for everyone, but too many people do not plan. They put off estate planning because they suppose that:
- They are not old enough.
- They do not possess enough.
- It’s going to be either costly or complicated.
- They will have plenty of time to do it later.
- They lack knowledge where to start or where to seek assistance or
- They just do not want to think about it.
Then, when something happens to them their families have to run around and fix the situation.
Unfortunately, we cannot successfully predict how long we will live, and illness and accidents happen to people of all ages. Again, there is the likelihood that we may be incapacitated from making decisions on our own. Therefore, the best time to plan your estate is now. You can put something in place now and change it later. It helps not to get caught off-guard and unprepared when incapacity or death strikes.
Estate planning is a continuous process and not a one-time activity. You should revise the plan on a regular basis and as your family and financial status (as well as the laws concerning the same) changes in your lifetime. It is one of the most thoughtful and considerate things you can do for your loved ones.
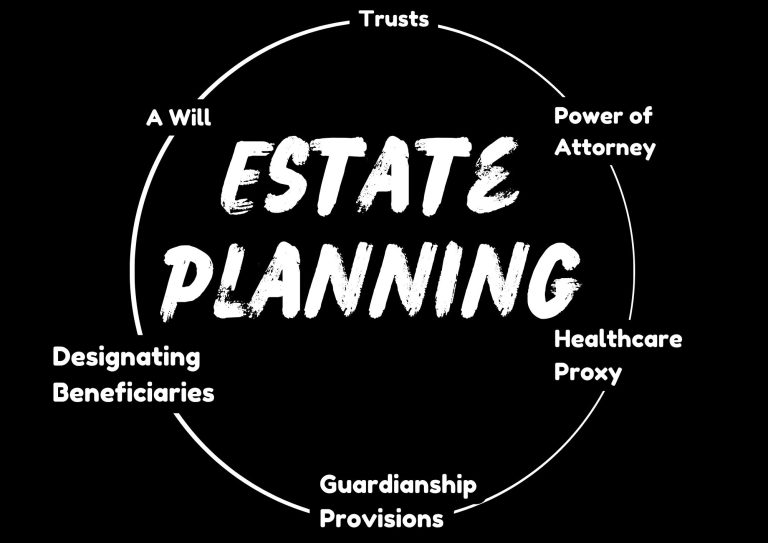
Key Elements of Estate Planning
Estate planning is a complicated process. It implies the consideration of essential factors to safeguard your personal belongings, preferences, and children to ensure that they are safeguarded and prosperous. Te following are the key elements of estate planning.
1. A will
This is a legal document, which, when properly drafted, effectively states how you wish for your affairs to be handled after your death. You can decide that so and so should be the beneficiary of such an asset or be given the responsibility of doing this or that. A will can also nominate guardians if you have children. It guarantees that their upbringing is in the hands of someone you prefer.

2. Trusts
This is an example of a legal structure that is widely used within estate planning. It caters to tax avoidance, provides for care, and distributes wealth. Through trusts, you can ensure the management of an asset without necessarily going to court.
3. Power of Attorney
This is an affidavit that enables a dependable person to make critical choices for you if you are not fit to do so by yourself. This is the trusted representative whose duty is to act in your behalf. For example, they can handle your investing.
4. Healthcare Proxy
This is a legal paper that authorizes someone to make health decisions on your behalf in case you cannot make them for yourself. This includes decisions about medical treatments, procedures, and interventions. Naming a healthcare proxy makes certain that your medical choices are implemented, and it provides your family direction during difficult moments.
5. Guardianship Provisions
If you are a parents with young children, you need to ensure that you decide who will look after your children in the event that you and/ or the other parent cannot do so. This way you are sure that your children with be with people you trust and those who also have the same set of principles, standards and beliefs as you.
6. Designating Beneficiaries
Lastly, you must determine who will benefit from your life insurance, retirement fund, bank accounts, and other possessions after you die. Periodic updating of the beneficiaries’ designations should necessarily be carried out, particularly after important occurrences in your life like marriage, divorce, or the birth of children.
Conclusion
Estate planning is a useful process that formalizes how your property will be protected, controlled, and divided when you die or are unable to handle your affairs yourself. An estate plan ensure that your wealth passes on in an organized manner, protect your loved ones and reduce the chances of conflicts or litigation. While wills, trusts, powers of attorney, healthcare proxies and provisions for guardianship of your children or wards are critical tools in protecting your estate, your intentions must be well understood by the relevant authorities.
Estate planning is not restricted to the elderly, and misfortune can strike at any time. So, begin this process at an early stage. Make the effort to create the plan and then periodically revisit and modify your estate planning documents. You can create a future for you and your family while encountering as few problems as possible.