Cryptocurrency or crypto, is an electronic currency used in trading and purchasing products and services in the same way as any other currency like cash. It’s also used for the speculative investment. It can be bought or sold with the purpose of making profits, like any other financial asset class like stocks. But the use of cryptocurrency is particularly a volatile investment class.
Cryptos do not have a physical form like official currency (like banknotes or coins) that one can touch and feel. Encryption algorithms and technologies, such as cryptography and blockchain, give these entities their names. These algorithms and technologies create these cryptocurrencies and also allow them to function both as a currency and as a virtual accounting system. That is why they don’t require a bank or financial institution to verify transactions. It means that one can send funds and the transaction is verified and put into a ledger known as a blockchain.
Blockchain is an immutable (unchangeable) record system that provides information about assets and transactions.
Popular cryptocurrencies include Bitcoin, Ethereum, Tether, USD coin, and XRP.
To use cryptocurrencies, you need a cryptocurrency wallet.
Cryptocurrency vs. traditional currency
- The government prints traditional currency as physical money in paper bills and coins, while cryptos are built using encryption algorithms and technologies.
- Cryptocurrencies are stored in digital wallets, so you can carry these paper bills and coins with you or put them in a bank or another financial institution.
- Crypto has no recourse in the event of a loss, while banks insure money kept in bank accounts against loss.
- Cryptocurrency has no government, bank, or financial institution controls. This decentralized entity has no central government as its issuing, backing, or governing authority. However, the government issues, supports and regulates traditional currency.
Brief overview of cryptocurrency
In 2009, a person – or group – using the pseudonym ‘Satoshi Nakamoto’ released Bitcoin. With Bitcoin, a cryptocurrency, a new genre of decentralised digital currencies came into being. Cryptocurrencies are based on the underlying concept of the blockchain.

Since then, the advancement in blockchain technology has led to the existence and growth of various cryptocurrencies and digital securities. A plethora of cryptocurrencies with unique characteristics and roles have emerged in the market.
There is an entire group of alternative cryptocurrencies commonly known as “altcoins.” Some individuals label them as “shitcoins.” These cryptocurrencies can be tailored and replicated by using open-source code. There are are 13,217 cryptocurrencies as of March of 2024. Over 80 digital currencies today have a market capitalization greater than $1 billion.
Some cryptos are traded for profit, fueling price surges. Cryptocurrencies have experienced some level of volatility as indicated by the growth and bursts and market crashes in different calendar years.
Today, there are thousands of blockchains around the world with different purposes, filled with countless references, data, and interactions. Some power Bitcoin, Litecoin, Tezos, and countless other digital currencies. Others have nothing to do with digital money. This technology has evolved from only being used for transactions to include various applications. This includes making supply chain more transparent, protecting health records and preventing fraud through more transparency in records.

How Cryptocurrency Works
The word “crypto” is derived from the term cryptography. It comprises the methodologies that can be employed to safeguard information such as the encryption algorithms, public and private keys, and hashing mechanism.
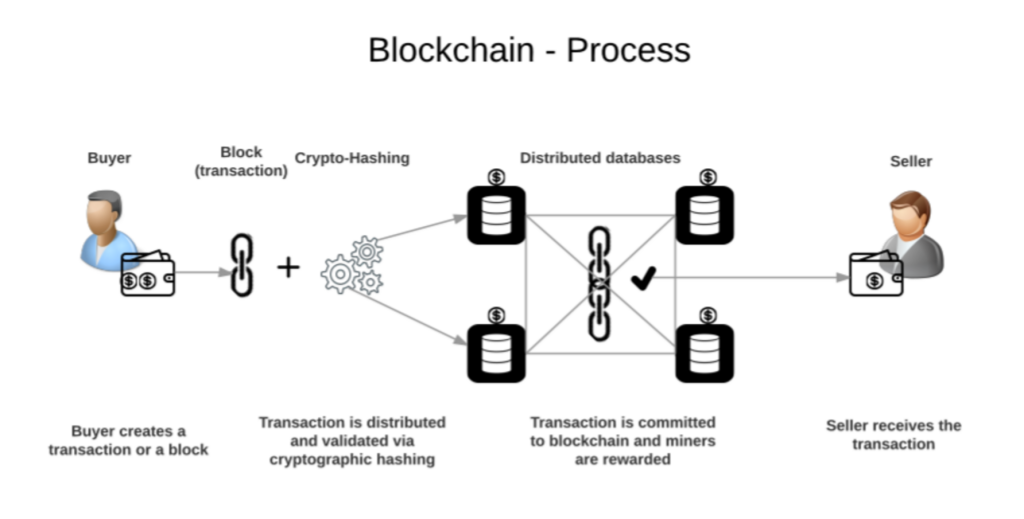
A blockchain is an open database with the particularity that data is shared and accumulated in blocks. These blocks are secure and and linked together through cryptographic techniques. Blockchains are mainly used as ledgers for transactions, though they can store diverse information.
Whenever you engage in a transaction within the blockchain, all the transaction particulars are meticulously documented in a block. A block resembles a cell in a spreadsheet. Multiple electronic devices, also referred to as the nodes, to confirm this information.
After a block is completed, the information it contains undergoes encryption. It is then transformed into a string of random letters and numbers known as the hash. This hash encapsulates all the data within the block. This implies that if there are any changes to the block’s data, then the hash will also change in some way.
Each block has the hash of the previous block, making a connection between the blocks. When organized this way, these series of blocks forms a chain.
Each new transaction is added to the ledger of every participant within the blockchain. It is impossible to change a transaction without adjusting subsequent blocks and getting the consent from the rest of the participants in the network. That is why cryptocurrency transactions are characterized by transparency, security, and immutability.
How to Generate Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency units are created through a process referred to as mining. Mining is the use of a sophisticated computing device or a cluster of such devices aided by unique software that checks and validates the transactions after which they are added to the blockchain.
Miners receive coins or tokens from the cryptocurrency industry as compensation for their efforts. The three consensus mechanisms include; proof of work, proof of stake, and proof of authority, which help in validating the transaction from the various participants.
- Proof of Work (PoW) is a process deployed by miners to verify transactions and add blocks to the block-chain through solving complicated mathematical problems. The miner who successfully solves the problem first is given cryptocurrency as a reward.
- Proof of Stake (PoS) is the consensus algorithm that decides who should validate transactions as a miner depending how much cryptocurrency they own. The more cryptocurrency you own, the higher your chances are of being selected. This process is called “staking.”.
- Proof of Authority (PoA) is a system of rules used for personal or consortium chains. It uses trusted nodes, which are called validators. They are appointed by the community administrator and are supposed to validate transactions and include them into the block chain. Validators have to ensure the security of the network.
Classification of Cryptocurrencies
Currently, there are about nine kinds of cryptocurrencies in the market. These include Stablecoins, Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs), Payment Tokens, Exchange Tokens, Utility Tokens, Security Tokens, Decentralised Finance (DeFi) Tokens, Asset-Sponsored or asset-back tokens, and Privacy Tokens.
This categorization of cryptocurrencies depends on a variety of factors, such as the mathematical formula or code, the purpose or use case, and the operational mechanisms.
1. Stablecoins
They are cryptos that are designed to hold a stable price over a given period of time. They are backed by assets that have a fixed price or assets with moderate volatility in their value like gold or fiat currency. Gold Coin (GLC) and Tether are two examples of stablecoins. Gold Coin (GLC) is backed by gold, while Tether is pegged to the USD at a 1:1 ratio.
2. A Non-Fungible Token (NFT)
It is a digital asset that certify ownership of unique items that cannot be traded in a similar manner to other goods. They represent many valuable assets that exist in digital and physical forms on the blockchain. Some of the items that can be represented by NFTs include art, photography, and videography, collectibles, real estate, virtual space, memes, GIFs, social media post, tweets, fashion, music, paintings, drawings, academic credentials, political memorabilia, films, sports collectibles, games, and other digital file forms. One popular use case of an NFT is the conversion of Jack Dorsey’s first tweet into an NFT.
3. Payment tokens
These enable people to conveniently use cryptocurrencies to buy and sell goods and services. They enable people to transact on the digital marketplace without having to go through a third party such as a bank.
Exchange tokens are used in buying, selling, and trading of other tokens within a cryptocurrency exchange platform. These exchanges are online platforms for buying and selling tokens as well as exchanging them. Examples of exchange tokens are Binance Coin, KuCoin Token, Gemini USD, and OKB.
4. Utility tokens
These are like a digital coupons or vouchers. They represent a value on the blockchain. They provide the token holder with a right of using an asset or receiving a product or service which is provided by the token creator. If you buy utility tokens, you can use them to gain access to your desired products or services. Some examples of utility tokens include FUN of Funfair, BAT of Basic Attention Token, Brick Legendary of Brickblock, TIM of Timicoin, SRN of Sirin Labs Token, and GNT of Golem.
5. Security tokens
These cryptos derive their value from real assets such as land, buildings, or shares among others. These tokens are governed by financial rules. They can be traded like other securities. The financial regulators have the duty to supervise the proper performance of the security token operations, safeguard the invested funds and investments, and penalize issuers if needed. Examples of security tokens are Sia Funds, Bcap, and Science Blockchain.
6. DeFi Tokens
They refer to open-source financial applications known as decentralized applications or dApps, which are built on blockchain technology. They offer you the independence to make decisions regarding your money as you wish. These tokens enable the users to transfer money from one person to another in different part of the world hassle free. They also provide opportunities to access international markets. Some of the Blockchain platforms that help in the working of DeFi applications include Ethereum, Stellar, Polygon, IOTA, Tron, and Cardano. Solana and Chainlink are two examples of tokens used in decentralized finance.
7. Asset-Backed Tokens
These are based on real-world assets including, currency, stocks, bonds, real estate, and other precious metals like gold. These tokens can be used to trade or represent physical commodities within blockchains. Some examples of asset-backed tokens include OilCoin, Petroleum, and Ziyen Inc.’s Oil token.
8. Privacy tokens
These are cryptocurrencies whose primary focus is on user anonymity. Their privacy features are way better than other popular coins like Bitcoin, or any other for that matter. Some of the privacy tokens are Monero, Zcash, Dash, Horizen, Beam, and Verge.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency presents a fresh perspective when it comes to digital or virtual money. Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum are based on encryption algorithms and the technology of blockchain which has given a new perception on how we perceive and transact value. From stablecoins to privacy tokens, the variation in cryptocurrencies ensures that the digital economy satisfies various demands. It is essential that you understand what cryptocurrencies are, how they are created, and how the consensus mechanisms work in this emerging field. It is therefore vital that the you and other stakeholders remain informed and up to date to fully realise the benefits of cryptocurrencies in a constantly transforming financial landscape.


